how do glasses work physics
S M and L and they are responsible for identifying the colors blue green and red respectively. The eyeglass lens is simply used to create an image of the object at a distance where the nearsighted person can see it clearly.
How the eye works is that natural lenses are able to bend the light that passes through it into a clear right-side-up image.
. The lens of the eye will need to compensate for closer objects. The screen actually displays two images and the glasses cause one of the images to enter one eye and the other to enter the other eye. This can be seen in the figure below.
These glasses are used when two images are projected superimposed onto the same screen through orthogonal polarizing filters Usually at 45 and 135 degrees. The third way your brain percieves distance is it gauges the lenses in your eye. How do glasses use waves to work.
This in turn becomes a measure of how far away an object is. There are three types of cones. When a beam of light passes through any curved piece of glass it has a tendency to either expand the beam and spread it out or make the beam narrower eventually into nothing then expand again.
For glasses that correct for near sighted people this also means a reduction in size of the image on the retina. Polarized sunglasses work by having a special molecular structure in the lenses. With this orientation of the lenses the light waves reflected by a horizontal surface like water windshields or the street will not glare at you anymore.
Both medium and frequency affect how much radiation is attenuated. Sunglasses attenuate sunlight lead attenuates x-rays and human bodies attenuate the millimeter wave. In most cases the orientation of the polarized lenses is vertical.
Because of the different wavelengths of light each color is refracted a different amount. Our eyes detect colors using cones. The attenuation of electromagnetic waves is due to the absorption and scattering of photons.
Im not talking about the image height. Light hits the glass at an angle and it. The viewer wearing linearly polarized glasses can see only one image in each eye the one which has same polarizing angle.
In these there are two types Linearly Polarized Glasses. It uses the slower speed of light in glass to its advantage by refracting the light twice. For contacts which are much closer to the lens the size distortion is much less.
When you have both eyes open you dont need the bobbing as you already have input from two different perspectives and a brain well versed in interpreting it. Glasses are comprised of lenses that bend light. A magnifying glass is usually a convex lens a lens that bulges outwards made of either glass or plastic.
Glasses are cut to change the focal length of the light entering the eye so it hits the focal point properly and the wearer can see without blurring. In a movie theater the reason why you wear 3-D glasses is to feed different images into your eyes just like a View-Master does. This way the light waves reflected by a surface at a certain angle get blocked out.
Glasses with Polarizing Filters. The red and blue lenses filter the two projected images allowing only one image to enter each eye. The blue cones usually operate disjointly whereas for most people the red and green cones might have working regions that overlap.

Subtracting Vectors That Are Antiparallel Vector Subtraction Of Antiparallel Vectors More At Plainphysics Com Subtraction Physics Math

Do Yellow Bug Light Bulbs Work 1000bulbs Com Blog Electromagnetic Spectrum Visible Light Visible Light Spectrum

Thin Lens Sign Conventions Article Khan Academy

Lens Meaning Principles Manufacture Facts Britannica
26 2 Vision Correction College Physics Chapters 1 17

Prism Lenses For Your Eye Glasses Eye Facts Computer Vision Syndrome Physics Notes

6pc Optical Lens Set 2 200mm 300mm 500mm Focal Lengths 3 Double Convex 3 Double Concave Optical Lens Optical Physics Classroom

Why Do You Wear Glasses 4th Grade Science Lessons Interactive Notes Hand Lens
Physics Tutorial Refraction And The Ray Model Of Light

How Do Eyeglasses Work Infographic

How To Get The Thinnest Lenses For Your Prescription Zenni Optical Eyeball Diagram Eye Sight Improvement Physics
Creating A Set Of Rainbow Fringes Using A Diffraction Grating Physics And Mathematics Physics Teaching Ideas Physics Classroom

Thin Lens Sign Conventions Article Khan Academy
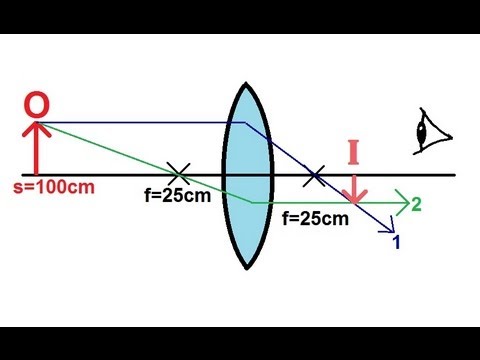
Physics Optics Lenses 1 Of 4 Converging Lens Youtube

Torque And Rotational Equilibrium Teresa Glasses S Investigations Simple Machines Physics Simple Machines Activities
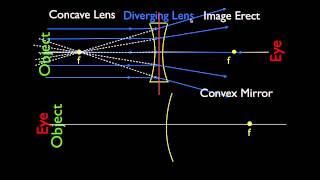
Concave And Convex Lenses And Mirrors Parallel Light Rays Convex Mirror Concave Mirrors Concave

